Amazon OTP Shutdown: Secure Your Account Now!
Is your online security truly secure, or are you unknowingly leaving the door open for cyber threats? Amazon's recent shift away from one-time password delivery underscores the urgent need to re-evaluate our digital safety protocols.
In an increasingly interconnected world, the threat landscape is constantly evolving. Major tech companies, like Amazon, are proactively adapting their security measures to protect their vast user base from sophisticated attacks. This move away from traditional one-time passwords (OTPs) represents a strategic shift towards enhanced account protection, reflecting a deep commitment to safeguarding the data of millions of consumers and businesses worldwide. This article will delve into the core reasons behind this change, explore its implications, and provide a practical guide for securing your online accounts.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Topic | Amazon's Enhanced Account Security Measures |
| Objective | To understand the shift away from SMS-based OTPs and the adoption of more secure authentication methods. |
| Key Changes | Disabling one-time password (OTP) delivery via SMS, promoting authenticator apps, hardware security keys, and biometric authentication. |
| Impact | Affects millions of Amazon users and businesses, requiring adaptation to new authentication methods. |
| Benefits | Enhanced account security, reduced risk of unauthorized access, and protection against cyber threats. |
| Reference | Amazon Official Website |
One-Time Passwords (OTPs) have been a foundational element of two-factor authentication (2FA) systems for many years. They were designed to provide a secondary layer of defense, going beyond the standard password to verify a user's identity when logging into accounts. Historically, Amazon, like many other online platforms, has relied on OTPs, delivering them primarily via SMS, email, or authenticator apps. This approach, while adding a layer of security, has faced vulnerabilities as cyber threats became more sophisticated.
- Priscilla Love Van Winkle Bourbon Legacy Impact You Need To Know
- Trending Mms Strategies Amp Trends For 2024 Amp Beyond
Understanding OTPs in Authentication
The primary function of an OTP is to make unauthorized access more difficult, even if an attacker manages to obtain a user's password. However, the reliance on SMS-based OTPs, in particular, has exposed weaknesses. SIM swapping, where attackers reroute SMS messages to their own devices, has become a significant threat. Furthermore, SMS messages can be intercepted through various means, compromising the security of the OTP itself. These vulnerabilities necessitate a more robust approach to user authentication.
Amazon's decision to disable SMS-based OTP delivery is in line with industry-wide trends that emphasize more secure authentication methods. As the sophistication of cyber threats escalates, companies must adapt to protect their users. This shift reflects a proactive strategy aimed at minimizing risks and ensuring the ongoing security of user accounts.
The impetus behind Amazon's decision to disable one-time password delivery is rooted in its unwavering dedication to user security. This change is not merely a reaction to existing threats but a forward-thinking approach to anticipate and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Several key factors have fueled this decision, primarily the escalating prevalence of sophisticated cyberattacks and the inherent limitations of SMS-based OTPs.
- Dell Curry How He Shaped Ayeshas Success Inspired Generations
- Dwight Schultz From Ateam To Theater A Closer Look
Cybersecurity Threats
The move to eliminate SMS-based OTPs is a direct response to the following threats:
- SIM Swapping Attacks: This malicious technique allows hackers to intercept OTPs by gaining control of a user's phone number. Attackers convince mobile carriers to transfer the victim's number to a SIM they control, granting them access to OTPs sent via SMS. This can lead to account breaches, financial losses, and identity theft.
- Phishing Attempts: Phishing attacks are designed to trick users into revealing their OTPs. Cybercriminals often create convincing fake login pages or send deceptive emails, enticing users to enter their OTPs, thereby granting attackers access to their accounts.
- Malware and Spyware: Malicious software installed on compromised devices can capture OTPs. This includes keyloggers, which record keystrokes, and other forms of spyware that monitor device activity and steal sensitive information.
By discontinuing one-time password delivery, Amazon aims to proactively eliminate these vulnerabilities. This allows the company to guide its users towards more secure authentication methods, thereby reducing the attack surface for potential threats and bolstering the overall security posture of the platform.
The move to disable OTP delivery is not an isolated change; it is a key component of a broader strategy to enhance security measures across the Amazon ecosystem. The company is actively promoting alternative authentication methods that are designed to offer superior protection against evolving cyber threats.
Implementing Advanced Authentication
Amazon is actively encouraging users to adopt the following advanced security measures:
- Authenticator Apps: Apps like Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator generate time-based OTPs. These apps reside directly on a user's device and are not reliant on SMS delivery, therefore mitigating the risk of interception. The codes are time-sensitive and change periodically, making them difficult for attackers to reuse.
- Hardware Security Keys: Hardware security keys, such as those from YubiKey, offer a physical layer of authentication. These devices require physical interaction, such as pressing a button or inserting the key, to verify a login attempt. Hardware security keys are highly resistant to phishing attacks and provide a robust, secure option.
- Biometric Authentication: Fingerprint scanning and facial recognition are becoming increasingly popular as convenient and secure alternatives. These methods leverage unique biological traits to verify a user's identity, reducing the need for passwords and codes.
By promoting and integrating these methods, Amazon significantly reduces the risk of account compromise. This aligns with Amazon's commitment to maintaining the highest security standards and providing a safe and secure environment for its users.
With the phasing out of SMS-based OTPs, users must proactively explore and adopt alternative authentication methods to safeguard their Amazon accounts. The transition necessitates a shift in approach, moving away from a familiar, yet increasingly vulnerable, security measure towards more robust options.
Authenticator Apps
Authenticator apps are a crucial component of the new security paradigm. They generate time-based OTPs that are synchronized with Amazon's servers. This approach eliminates the inherent vulnerabilities of SMS-based delivery, dramatically decreasing the risk of interception. Popular options include:
- Google Authenticator: Widely used and supported across various platforms, Google Authenticator is a free and easy-to-use option.
- Microsoft Authenticator: Similar to Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator offers a reliable way to generate time-based OTPs.
- Authy: Authy is a versatile authenticator app that supports multiple devices and offers cloud backup for added security.
Hardware Security Keys
Hardware security keys provide a physical layer of protection, requiring the user to physically interact with a device to authenticate login attempts. These devices are highly resistant to phishing attacks, making them a preferred choice for many security-conscious users.
The benefits of using hardware security keys include:
- Enhanced Security: They are highly resistant to phishing attacks, as attackers cannot access the key's security features remotely.
- Ease of Use: They are typically easy to set up and use, requiring only a simple insertion or tap to authenticate.
- Platform Compatibility: Many hardware security keys support various online services and platforms.
The decision to disable one-time password delivery has significant implications for both individual users and businesses that depend on Amazon's services. A clear understanding of these impacts is essential for a smooth and effective transition.
For Individual Users
Individual users might face initial challenges in adapting to new authentication methods. However, the long-term benefits of enhanced security greatly outweigh any temporary inconvenience. Users are encouraged to:
- Familiarize themselves with authenticator apps and hardware security keys: Experiment with different methods to determine which works best for their needs.
- Update their security settings promptly: This includes enabling MFA using authenticator apps or setting up hardware security keys.
- Stay informed about the latest security best practices: Regularly reviewing their account's security posture helps them stay protected.
For Businesses
Businesses that integrate Amazon services into their operations must update their authentication protocols. The transition requires careful planning and execution to ensure continued service and operational security. Businesses should:
- Conduct a comprehensive security audit: Identify vulnerabilities and areas needing updates.
- Train employees on using authenticator apps and hardware security keys: Ensure everyone understands the new procedures.
- Update internal systems to support advanced authentication methods: This may require software and infrastructure upgrades.
- Monitor account activity closely: Detect and respond to potential threats proactively.
Adapting to Amazon's decision to disable one-time password delivery requires a proactive and informed approach. Users must understand the steps involved to ensure a smooth and secure transition. A clear, step-by-step guide will help both individuals and businesses navigate this change effectively.
Steps for Individual Users
Follow these straightforward steps to secure your Amazon account:
- Enable an Authenticator App: Install an authenticator app (Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy) on your mobile device.
- Link the Authenticator App to Your Amazon Account: Follow Amazon's instructions to link the app to your account. This will usually involve scanning a QR code.
- Consider Purchasing a Hardware Security Key: For enhanced security, consider purchasing a hardware security key like YubiKey and setting it up with your account.
- Regularly Review Your Account's Security Settings: Check your security settings periodically to confirm that your account is configured correctly and aligned with best practices.
Steps for Businesses
Businesses need a structured approach to ensure business continuity and robust security:
- Conduct a Security Audit: Evaluate your current authentication processes and identify areas requiring improvement.
- Train Employees: Provide comprehensive training on using authenticator apps and hardware security keys.
- Update Internal Systems: Modify systems to support advanced authentication. This may involve system upgrades and integration efforts.
- Monitor Account Activity: Closely monitor all account activity to detect and respond to any potential threats. Implement a system for proactive threat detection.
Securing your Amazon account goes beyond simply adopting alternative authentication methods. Implementing these best practices helps to fortify your overall account security posture and minimize the risk of compromise. A multifaceted approach is crucial.
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Employ complex passwords that are difficult to guess. Use a password manager to generate and store passwords securely.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Everywhere: Turn on MFA for all accounts that support it. This includes not only Amazon but other critical online services.
- Regularly Review Account Activity: Frequently check your account activity for any unusual or suspicious behavior.
- Keep Software and Devices Updated: Ensure that all software and devices are running the latest security patches. Timely updates patch vulnerabilities.
- Avoid Clicking on Suspicious Links: Be cautious of links in emails or messages that you don't trust. Verify the sender and destination before clicking.
By implementing these best practices, you significantly reduce the risk of account compromise, creating a safer and more secure online experience.
Here are some frequently asked questions to provide clarity on Amazon's decision:
Why is Amazon disabling one-time password delivery?
Amazon is discontinuing SMS-based OTP delivery to boost account security, specifically addressing the vulnerabilities associated with this method. The company aims to shift users toward more robust authentication measures.
What are the alternatives to one-time passwords?
Alternatives include authenticator apps (Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, Authy), hardware security keys (YubiKey), and, potentially, biometric authentication methods (fingerprint or facial recognition).
Will this change affect my existing accounts?
Yes, all Amazon accounts will need to transition to these alternative methods to maintain secure access. Users will need to adjust their security settings accordingly.
Cybersecurity statistics emphasize the importance of adopting advanced authentication methods. These insights highlight the evolving threat landscape and the significance of Amazon's decision.
- Phishing Attacks: According to recent studies, 68% of businesses experienced phishing attacks in 2022. Phishing continues to be a prominent method used by attackers to gain access to accounts.
- SIM Swapping Attacks: SIM swapping attacks increased by 220% between 2020 and 2021. This significant increase highlights the risk associated with SMS-based OTPs.
- Multi-Factor Authentication Effectiveness: Multi-factor authentication significantly reduces the likelihood of account compromise. Implementing MFA can reduce the risk of account compromise by up to 99.9%.
These figures underscore the growing need for robust security measures and the significance of Amazon's move to phase out one-time password delivery. The data reinforces that strong authentication is critical.
- David Paul Olsen Movies Tv Shows You Need To Know
- Vad Seed Revolutionizing Agriculture For A Sustainable Future
Amazon Secure Delivery Password)

Amazon password for personal delivery
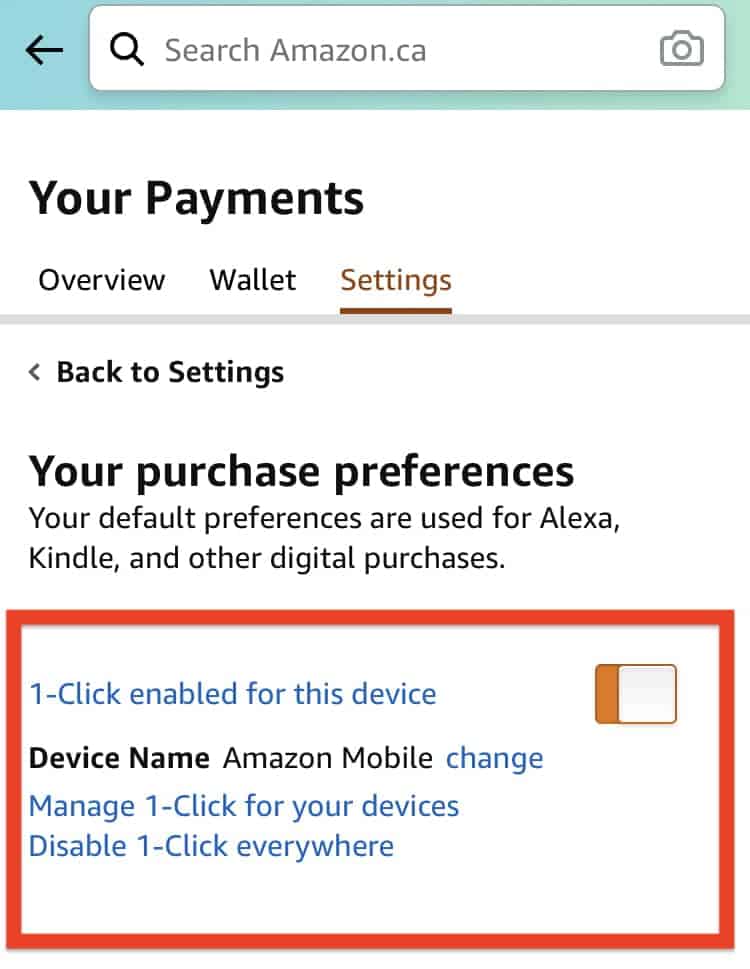
Amazon disable one click fecollast